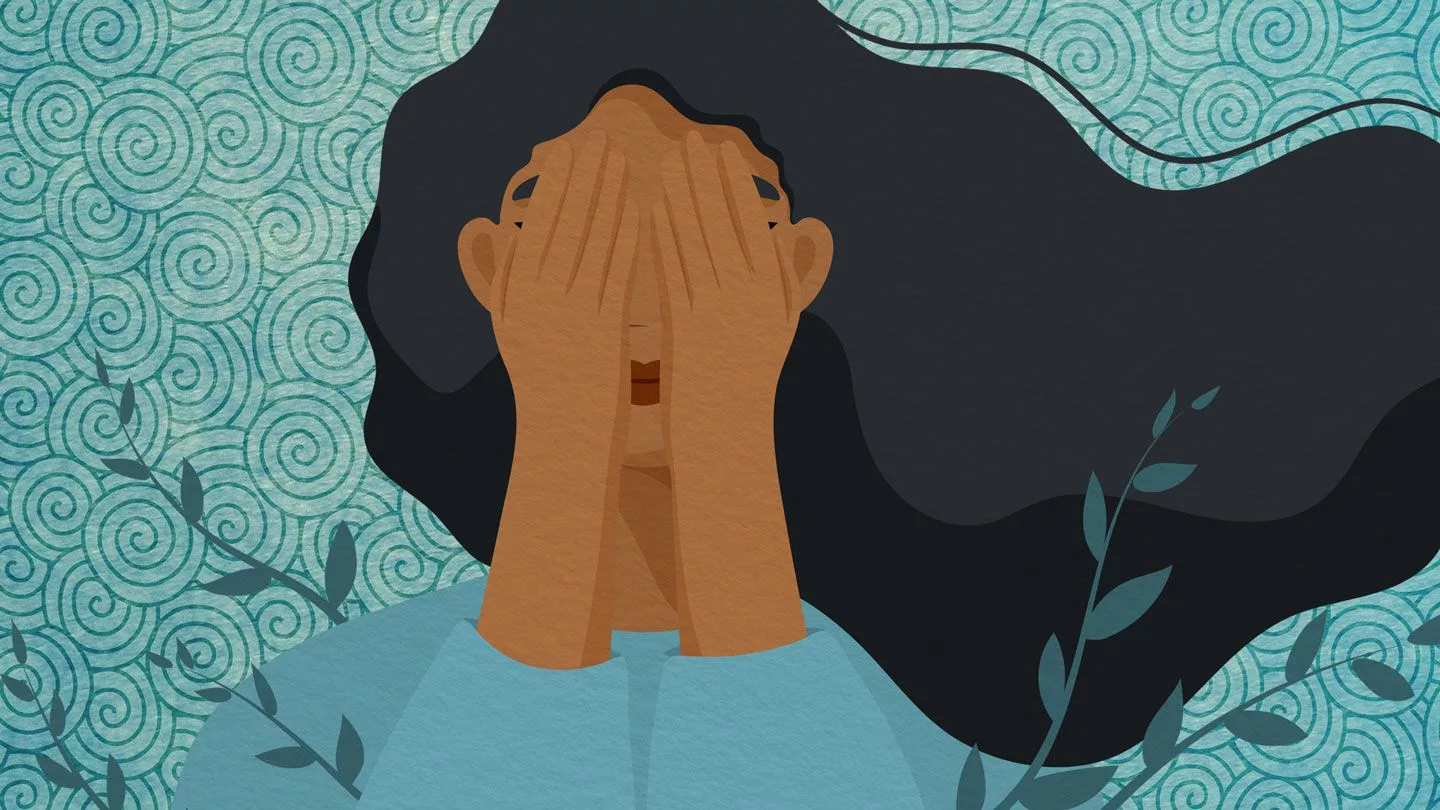
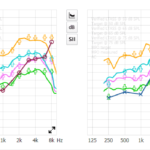
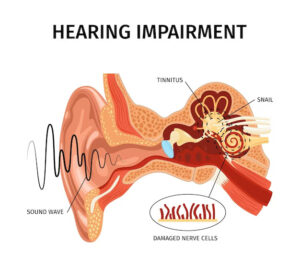
Hearing loss can indeed lead to anxiety and depression, as research has shown that individuals with hearing loss are more likely to experience these mental health issues. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that individuals with hearing loss were more likely to report symptoms of anxiety and depression than those with normal hearing (Lin et al., 2011).
One potential reason for this link is the social isolation and communication difficulties that can result from hearing loss. Individuals with hearing loss may feel isolated from others and may struggle to participate in conversations, which can lead to feelings of loneliness and social isolation (Bess et al., 2016). This isolation can also impact an individual’s ability to engage in meaningful activities and hobbies, leading to a decrease in quality of life (Gates et al., 2013).
Furthermore, hearing loss can also lead to cognitive decline, including decreased memory and problem-solving abilities (Lin et al., 2011). This cognitive decline can contribute to feelings of anxiety and depression as individuals may struggle with everyday tasks and decision making.
It is important for individuals with hearing loss to seek treatment, such as hearing aids or other assistive devices, to improve their communication abilities and social engagement. This can help to mitigate the negative mental health effects of hearing loss. Additionally, seeking therapy or counseling may be beneficial for individuals who are struggling with anxiety and depression related to their hearing loss.
Overall, it is clear that hearing loss can lead to anxiety and depression, and it is important for individuals with hearing loss to seek treatment and support to address these mental health concerns.
References:
Bess, F. H., Dodd-Murphy, J., & Parker, R. A. (2016). Psychological and social consequences of hearing loss in older adults: A review. Psychological Bulletin, 142(2), 121-143.
Gates, G. A., Giovannetti, T., & McCurry, S. M. (2013). Hearing loss and cognitive decline in older adults: A systematic review. JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, 139(8), 819-825.
Lin, F. R., Metter, E. J., O’Brien, J. L., Fozard, J. L., Zonderman, A. B., Ferrucci, L., & Resnick, S. M. (2011). Hearing loss and incident dementia. Archives of Neurology, 68(2), 214-220.